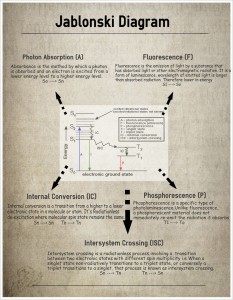
Jablonski Diagram
1
Photon Absorption (A) Fluorescence (F)
• Absorbance is the method by which a photon Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that
is absorbed and an electron is excited from a has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a
lower energy level to a higher energy level. form of luminescence, wavelength of emitted light is longer
So —> Sn than absorbed radiation. Therefore lower in energy
S1 So
I
exc vibrational states •
(excited rotational states not show*
A = photon absorption
F = fluorescence (emission)
P – phosphorescence
S – singlet slate
T – triplet State
IC – internal COnVersion
ISO interSyStern Crossing
•
electronic ground state •
Internal Conversion (IC) • Phosphorescence (P)
• Phosphorescence is a specific type of
ernal conversion is a transition from a higher to a lower photoluminescence.Unlike fluorescence,
tronic state in a molecule or atom. It’s Radiationless a phosphorescent material does not
xcitation where molecular spin state remains the same. immediately re-emit the radiation it absorbs
Sn —> Sn In —> In TI —> To
Intersystem Crossing (ISC)
Intersystem crossing is a radiationless process involving a transition
between two electronic states with different spin multiplicity i.e When a
singlet state non-radiatively transitions to a triplet state, or conversely a
triplet transitions to a singlet, that process is known as intersystem crossing.
Sn —> Tn Tn —> Sn